Once-A-Night Formulation of Sodium Oxybate Improves Excessive Daytime Sleepiness and Reduces Catplexy in Narcolepsy
Data from a pivotal phase 3 clinical study published in Sleep reveal that an investigational formulation of sodium oxybate (FT218; Avadel Pharmaceuticals, Dublin, Ireland), taken only once nightly, improved excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) and cataplexy in adults with narcolepsy.
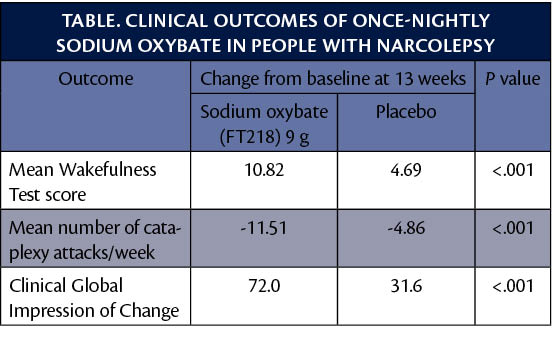
Topline data from the REST-ON trial (NCT02720744) showed that the 9 g dose of once-nightly sodium oxybate demonstrated a highly significant and clinically meaningful improvement compared to placebo across all 3 co-primary endpoints: results of the Maintenance Wakefulness Test and the Clinical Global Impression-Improvement Scale, and the mean number of weekly cataplexy attacks.
“The publication of the REST-ON trial results in the peer-reviewed journal Sleep validates the potential of FT218 as a once-at-bedtime option that could, if approved, transform the treatment landscape for adults suffering from the burdensome symptoms of narcolepsy,” said Jennifer Gudeman, PharmD, vice president of medical and clinical affairs, Avadel. “We believe FT218 has tremendous potential to provide clinically meaningful results for people with narcolepsy.”
Overall, the 9 g dose of FT218 was generally well-tolerated, with the most common adverse reactions for sodium oxybate occurring at low frequencies (nausea 1.3%, vomiting 5.2%, decreased appetite 2.6%, dizziness 5.2%, somnolence 3.9%, tremor 1.3%, and enuresis 9%).
After analysis showed statistically significant clinical improvement of the 9 g dose, the same analyses were conducted for the 7.5 g and 6 g doses which also provided statistically significant improvments in wakefulness, cataplexy, and clinical global impression.
