Cognitive Symptoms After Mild COVID-19 Correlated With Immunologic Biomarkers in Cerebrospinal Fluid
A clinical study found higher levels of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) immune activation and immunovascular markers in people with cognitive effects of post-acute of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC), also known as long COVID. C-reactive protein (CRP) and amyloid A levels were significantly higher in those with vs without cognitive symptoms. Differences in the CSF levels of vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) correlated with the onset of cognitive symptoms.
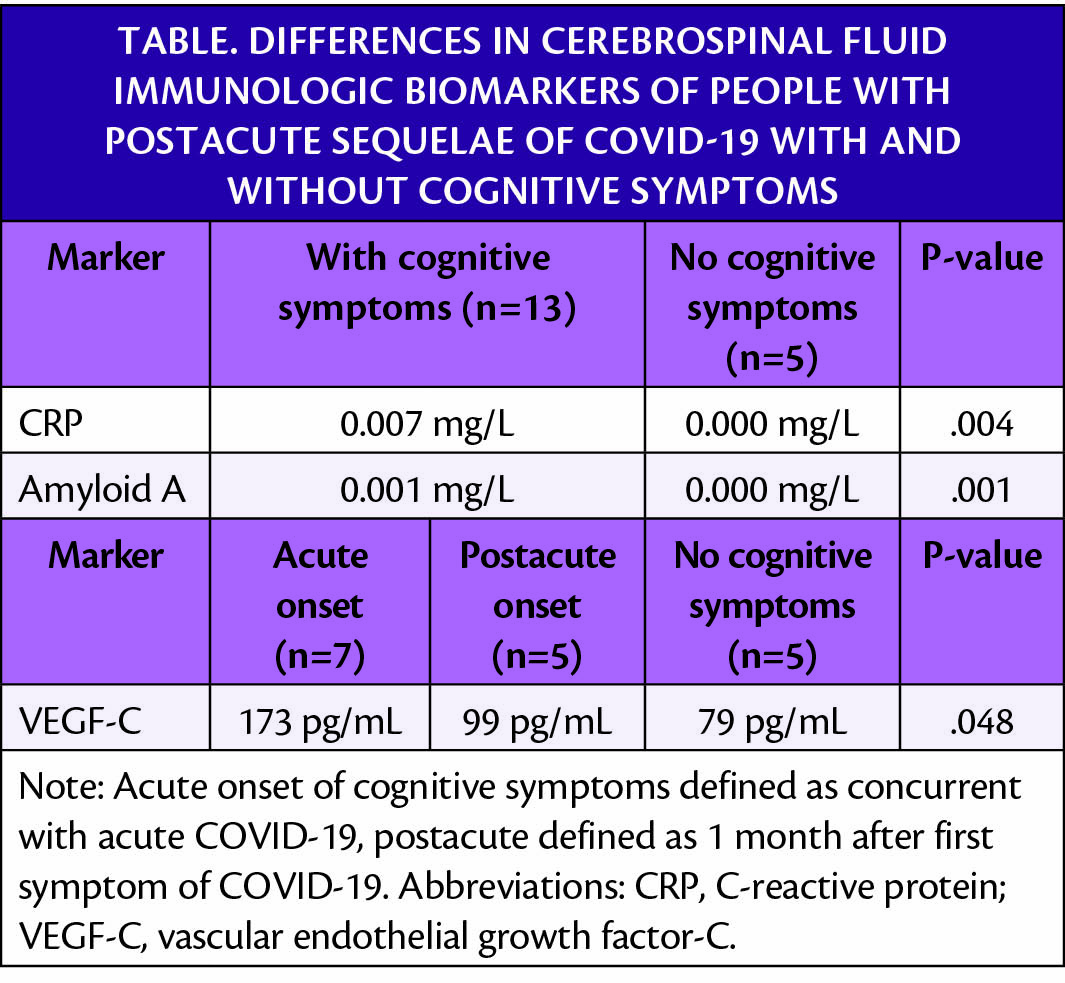
Higher levels of interleukin g inducible protein, VEGF-C and its soluble receptor 1 (VEGFR-1) were also observed in those with cognitive symptoms with any time of onset, but did not reach statistical significance. Higher levels of IP-10 (P=.030), IL-8 (P=.048), placental growth factor (P=.030), and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1; P=.045) were also seen in people with acute-phase onset of cognitive symptoms vs those with no cognitive symptoms.
Lead investigator, Dr. Joanna Hellmuth of the UCSF Weill Institute for Neurosciences Memory and Aging Center in San Francisco, noted, "this small study suggests there are differences in cerebrospinal fluid inflammatory markers in people who have persistent COVID-associated cognitive changes.It also implies there may be biological distinctions between patients with acute vs delayed onset cognitive changes after COVID. Patients often seek any emerging knowledge of this condition, as many face 'medical gaslighting' by loved ones, friends, and clinicians who may assume these milder executive functioning issues (compared with dementia) do not reflect a true neurologic condition."
Participants (n=33) in this study all had mild cases of COVID-19 that did not require hospitalization and positive tests for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Those with cognitive symptoms of PASC (n=23) were compared with those who did not have cognitive symptoms on structured neurocognitive tests. In 18 participants, (13 with cognitive symptoms, 5 without), cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was collected a median 10.2 months after their first COVID-19 symptom.
These findings are being presented at the American Academy of Neurology Annual Meeting, April 2-7, 2022 in Seattle, WA.
